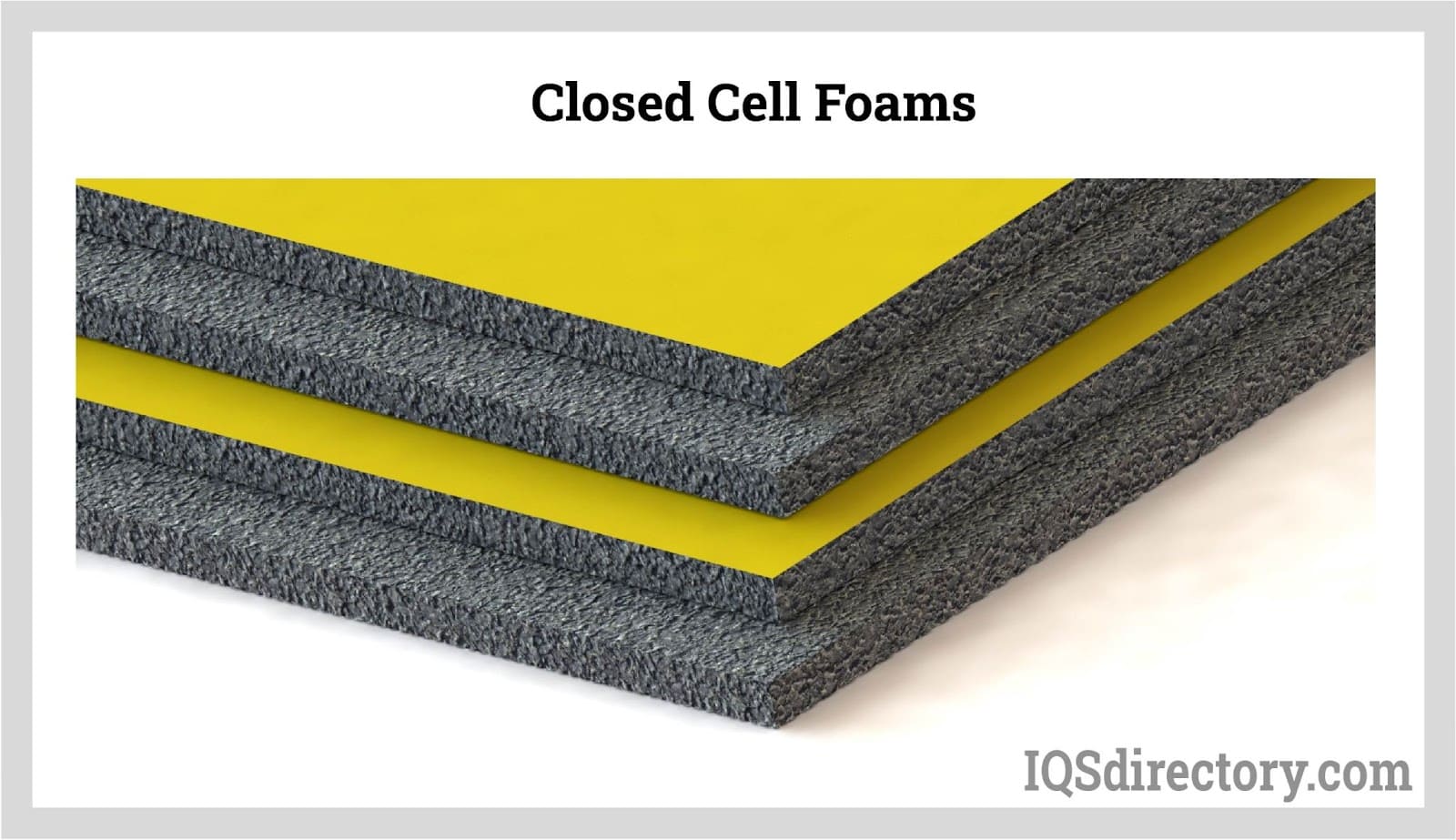
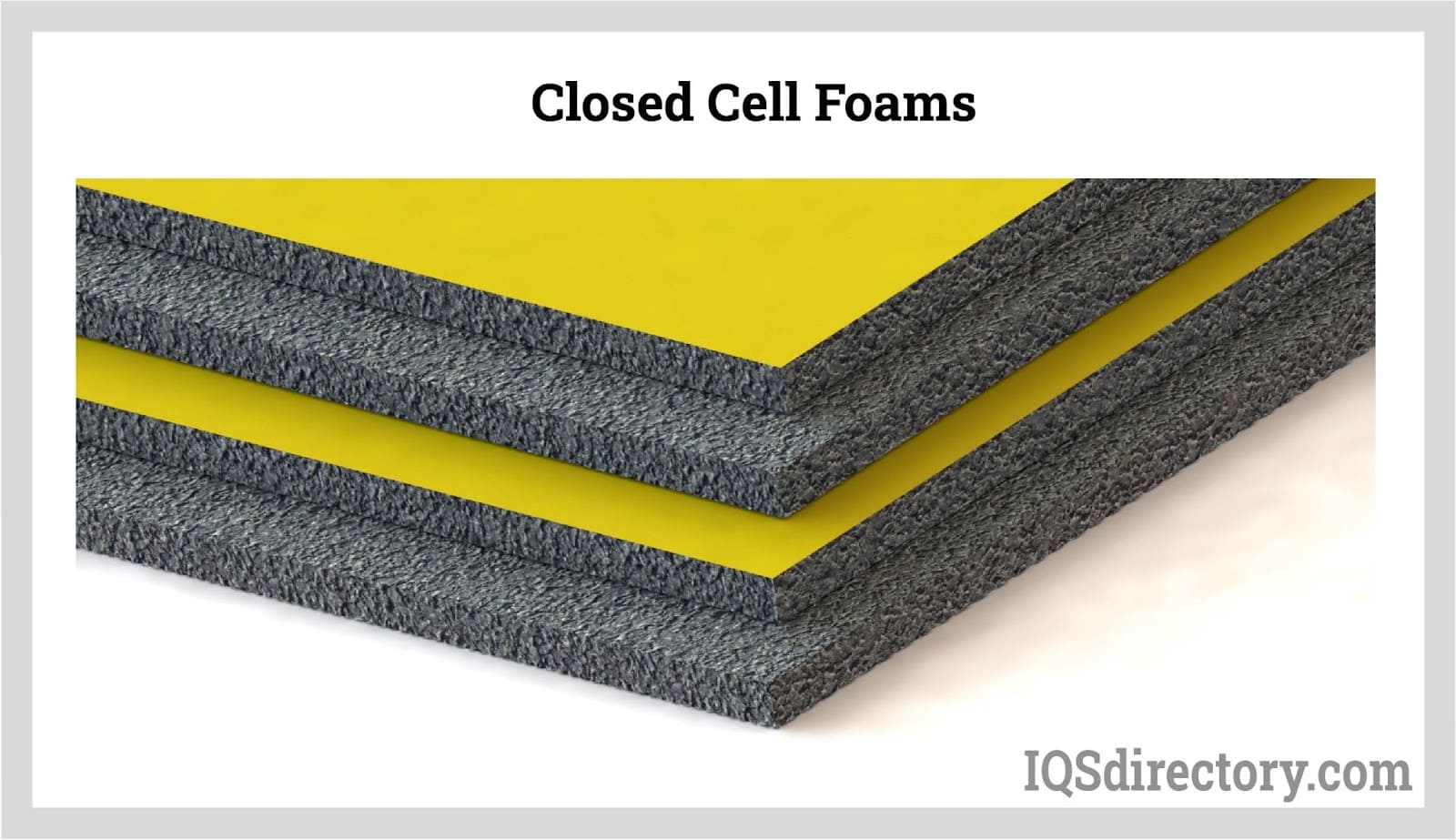
Closed-cell foam is a robust and flexible plastic rubber material with internal pores or cells. Closely spaced but unconnected, these closed-cell foam’s internal cells are located next to one another; the structure is comparable to a net packed with balloons.. The cells of this foam resemble tiny gas-filled bubbles, setting it apart from other foams. Closed-cell foam comes in various forms and sizes, is extremely resilient, and is waterproof. In addition, closed-cell foam comes in a huge range of densities and materials. Read More…
The applications for foam fabricating are only limited by one’s imagination; that is our slogan at American Excelsior. We are a foam supplier who offers many different foam cushions & foam padding for over a dozen industries.
Since 1992, Flextech has delivered innovative, custom engineered foam solutions. We combine our engineering and design services with our unique foam lamination, fabrication, and thermoforming capabilities, to provide quality foam components to a diverse customer base. Our customers include OEM’s in the medical, industrial, military, aerospace and consumer products markets. We invite you to...
Deluxe Packaging works hard to always create cost-effective solutions and services for our clients better than anyone else. We offer a full array of high quality products, including polyurethane foam, polystyrene foam, and polyethylene foam. Our products are customizable to match a product’s fragility and size. Deluxe Packaging is your complete packaging solution provider for all of your...

Here at Thrust Industries we provide die cut foam that comes in a variety of shapes and configurations. We die cut foam from a number of materials including: urethane, PVC, polyester, neoprene, ether, cellular, volara, and much more.
At Melmat, Inc., we specialize in custom foam fabricating solutions designed to meet the diverse needs of industries requiring reliable protective packaging, cushioning, and insulation. With decades of experience, we take pride in engineering foam products that balance precision, durability, and performance.

More Closed Cell Foam Companies

Manufacturing Process Of Closed-Cell Foam
Closed-cell foam—one of the most versatile and high-performance foam materials used today—is manufactured using advanced techniques that ensure its renowned structural integrity and durability. The closed-cell foam production process involves introducing a gas, typically nitrogen or carbon dioxide, under high pressure into a variety of rubber and plastic compounds. This creates a compact, bubble-wrap-like structure where individual cells are tightly packed and sealed off from one another, giving closed-cell foam its unique set of properties.
Manufacturers employ two main approaches in the closed-cell foam fabrication process:
- Direct Gas Exposure: The base material is exposed directly to high-pressure gas during the liquid or semi-liquid phase, allowing uniform cell formation.
- Use of Blowing Agents: Gas-forming chemical agents are blended into the material, releasing gas during curing or heating, which forms the closed cellular structure.
This closed-cell foam manufacturing process can be customized to create a wide range of foam grades, densities, and thicknesses, making closed-cell foams highly adaptable for various industrial, commercial, and consumer applications. Industries such as automotive, medical, sports, packaging, marine, and construction rely on closed-cell foam for its exceptional insulation, shock absorption, and moisture resistance. Whether you’re seeking foam for protective packaging, thermal insulation, or specialty engineering, closed-cell foam can be precisely engineered to meet diverse performance specifications.
Are you interested in learning more about how closed-cell foam is manufactured for your specific application? Contact a closed-cell foam supplier today to discuss custom fabrication options and technical requirements.
Types Of Closed Cell Foams
Closed-cell foams are available in an extensive variety of formulations, shapes, sizes, and densities, each engineered for specific mechanical, thermal, and chemical performance. The terminology can sometimes overlap, as many closed-cell foam types share similar properties, but subtle differences in manufacturing and material composition lead to distinct advantages and industry-specific use cases. Understanding the range of available closed-cell foams is crucial for selecting the right material for your project.
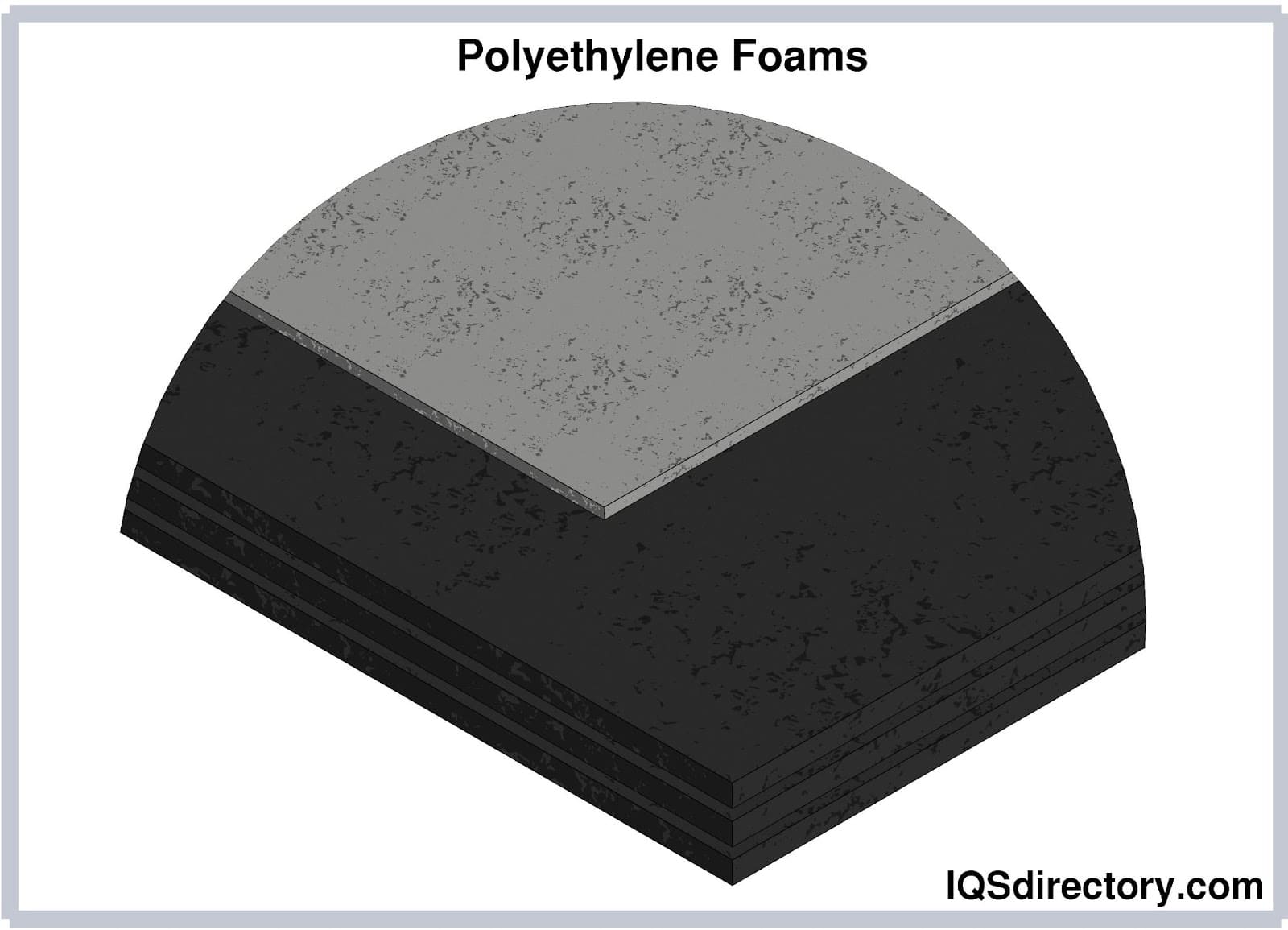
Polyethylene Foam
Polyethylene foam (often known as ethafoam) is a popular closed-cell foam material valued for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, durability, and resistance to moisture, chemicals, and stains. The tight cellular structure of polyethylene foam prevents liquid penetration, making it an ideal foam for applications where water resistance is critical.
Key attributes of polyethylene closed-cell foam include:
- Superior shock absorption for protective packaging and cushioning solutions
- Sound dampening and vibration control for industrial and automotive uses
- Buoyancy, making it suitable for flotation devices and marine components
- Lightweight and flexible for ease of fabrication and installation
Common uses for polyethylene foam include specialty packaging, sports and leisure equipment, medical device components, and arts & crafts supplies. It is also frequently used as a foam insulation material in construction and transportation.
Polyethylene Rolls
Polyethylene foam rolls are a form of closed-cell foam supplied in continuous lengths, making them easy to cut, shape, and install for large-scale or repetitive applications. Polyethylene rolls are available in a variety of thicknesses and densities, allowing engineers and designers to select the exact level of protection, insulation, or support required for their project.

Typical applications for polyethylene closed-cell foam rolls include:
- Pipe insulation and plumbing wrap for thermal efficiency and condensation control
- Medical and healthcare product cushioning
- Protective padding for sports equipment and gym flooring
- Automotive gaskets, seals, and vibration dampers
- Construction expansion joint filler
Looking to source polyethylene foam rolls for your next insulation or protective packaging project? Compare suppliers to find custom roll sizes and conversion services.
Cross-Linked Polyethylene
Cross-linked polyethylene foam (XLPE) is another advanced form of closed-cell foam. Through a process of cross-linking, the molecular structure of the foam is enhanced, resulting in a product that is tougher, more resilient, and more resistant to a wider range of chemicals and temperature extremes.
Advantages of cross-linked polyethylene foam include:
- Exceptional resistance to water, air, mold, and mildew
- Improved surface aesthetics, making it ideal for branded packaging, medical devices, and consumer products
- High thermal stability for HVAC insulation, refrigeration, and automotive interiors
- Lightweight with superior energy absorption properties
Common applications are found in building materials, protective packaging for electronics and high-value items, sports padding, and marine flotation equipment. Cross-linked polyethylene foam can be precisely fabricated to meet rigorous industry standards.

Polystyrene Foam
Polystyrene closed-cell foam is widely recognized for its rigidity, lightweight nature, and excellent thermal insulation properties. Available in various shapes such as blocks, spheres, and sheets, polystyrene foam comes in different densities to suit a range of uses from lightweight craft forms to structural insulation.
Polystyrene closed-cell foam is commonly used for:
- Building insulation panels and sheathing (such as EPS and XPS foam board)
- Protective packaging and shipping containers
- Model making and display applications
- Architectural detailing and signage
Wondering which type of closed-cell foam is best for your project? Contact our foam specialists for expert guidance on material selection, density, and custom fabrication options.
Other Closed-Cell Foam Types
Beyond the primary types listed above, the market offers additional closed-cell foam materials, including:
- Neoprene foam: Excellent resistance to oil, chemicals, and weathering. Used in wetsuits, gaskets, and industrial seals.
- PVC foam: Offers good flame resistance and cushioning, commonly used in automotive and construction applications.
- EVA foam: Known for its flexibility and shock absorption, ideal for footwear, sporting goods, and protective gear.
- Rubber-based closed-cell foams: Provide superior sealing, vibration isolation, and durability for harsh environments.
Each closed-cell foam variant has unique properties that can be optimized for your intended use. Ask us how to match foam material to your industry’s demands.
Advantages Of Closed Cell Foam
Why choose closed-cell foam for your next project? This advanced foam material offers a host of performance benefits that make it a top choice for demanding applications across numerous industries. Key benefits include:
- Waterproof and moisture-resistant: The tightly packed, sealed cell structure prevents the ingress of water, vapor, and most liquids, making closed-cell foam ideal for marine, HVAC, and outdoor applications.
- Self-cleaning pores: Closed-cell foam’s structure helps prevent glazing and makes it easy to maintain, with resistance to dirt, mold, and mildew.
- Lightweight yet strong: Closed-cell foams combine low density with excellent tear resistance, resulting in long-lasting, durable materials that are easy to handle and install.
- High rigidity and dimensional stability: The material’s increased stiffness helps it retain its shape under load, making it more durable than open-cell foam and less likely to deform over time.
- Outstanding insulation properties: Closed-cell foams provide exceptional thermal and acoustic insulation, functioning as an air barrier and reducing heat transfer and sound transmission in building envelopes, vehicles, and appliances.
- Superior energy absorption: Ideal for protective packaging, sports padding, and automotive crash components, closed-cell foam absorbs impacts and dissipates energy effectively.
- Chemical and oil resistance: Many closed-cell foams, such as polyethylene and neoprene, resist a broad range of chemicals, oils, and fuels, making them suitable for harsh industrial environments.
- Versatile fabrication and customization: Closed-cell foam can be die-cut, waterjet cut, CNC routed, laminated, or thermoformed to precise specifications, supporting custom solutions for OEMs and fabricators.
These advantages explain why closed-cell foams are the material of choice for thermal insulation, moisture barriers, flotation devices, shock-absorbing pads, and many more critical components. Looking for closed-cell foam properties for a specific application? Start your search here.
Common Applications and Use Cases for Closed-Cell Foam
Closed-cell foams are engineered to deliver performance across a broad spectrum of use cases. Here are some of the most common applications:
- Building and Construction: Used for wall insulation, roof insulation boards, soundproofing, expansion joint fillers, and waterproof barriers in both residential and commercial projects.
- Automotive Industry: Essential for vibration dampening, weatherstripping, gaskets, dashboards, and door panels, as well as protective packaging for parts during shipping.
- Marine Applications: Provides flotation, buoyancy, and moisture resistance in boat hulls, flotation devices, deck padding, and dock components.
- Medical and Healthcare: Used in orthotic and prosthetic padding, surgical positioning supports, and packaging for medical devices requiring sterile, moisture-resistant environments.
- Sports and Leisure: Found in gym mats, helmet padding, yoga blocks, protective gear, and swimming pool floats.
- HVAC and Refrigeration: Serves as thermal insulation for ductwork, pipe wrap, and vibration dampers.
- Industrial Manufacturing: Custom gaskets, seals, spacers, and protective packaging for sensitive equipment and electronics.
- Consumer Goods: Used in furniture padding, mattress toppers, footwear, and craft projects.
- Packaging Solutions: Closed-cell foam is widely used in the packaging industry for cushioning, vibration control, and shock absorption of fragile or valuable items during transit.
Curious about how closed-cell foam can enhance your product design or process? Explore our resources or request a custom quote from leading foam fabricators.
Disadvantages Of Closed Cell Foam
While closed-cell foam offers many high-performance benefits, it’s important to consider potential drawbacks when evaluating material options for your application:
- Lower shock absorption than open-cell foams: The dense, rigid cellular structure can provide less cushioning in high-impact applications compared to open-cell foam. Assess your impact and vibration requirements before choosing a foam type.
- Reduced breathability: Closed-cell foams are less permeable to air and moisture, which can be an advantage for insulation but may not suit applications needing ventilation or vapor permeability. For more breathable materials, see our guide on open-cell foams.
- Limited ability to fill small gaps: The rigidity of closed-cell foam can make it less effective at sealing small or irregular cavities compared to softer, more pliable foam alternatives.
- Higher density and weight: Compared to open-cell foam, closed-cell foam is stiffer, less flexible, and typically heavier, which may be a consideration for weight-sensitive or flexible applications.
- Potential for brittleness: In lower-quality formulations or extreme cold, closed-cell foam can become brittle and prone to cracking. Consult with your supplier on material specs for your environment.
- Cost considerations: Closed-cell foams are usually more expensive than open-cell alternatives due to the complexity of manufacturing and material performance. Evaluate your budget and performance needs accordingly.
Need help balancing benefits and trade-offs? Speak with our foam experts for material selection advice tailored to your project’s requirements.
Decision Factors for Selecting Closed-Cell Foam
Choosing the right closed-cell foam for your application involves careful evaluation of several key factors. Consider the following when specifying foam materials for your project:
- Density and thickness: Higher density foams are stiffer and provide better structural support, while lower density options offer more flexibility and lighter weight. Thickness can affect insulation value, cushioning, and overall performance.
- Thermal and acoustic performance: Assess R-value (thermal resistance) and sound attenuation properties for building, HVAC, and OEM applications.
- Chemical and moisture resistance: Some closed-cell foams are formulated to resist oils, fuels, solvents, or UV exposure. Match material to your application environment.
- Compression set and recovery: For gaskets, seals, and vibration control, select foams that maintain shape and rebound after repeated compression cycles.
- Fabrication and conversion capabilities: Make sure your supplier offers the necessary fabrication techniques, such as die cutting, laminating, or CNC routing, to achieve the desired part geometry and tolerances.
- Compliance and certifications: Verify that closed-cell foam materials meet relevant industry standards—such as UL, FM, ASTM, FDA, or RoHS—if required for your application.
- Cost and lead time: Request detailed quotes for material, fabrication, and delivery to ensure your project stays on budget and timeline.
Ready to compare closed-cell foam types and suppliers? Use our closed-cell foam supplier directory or request a quote for expert recommendations and fast sourcing.
Choosing the Correct Closed-Cell Foam Supplier
To achieve optimal results in your closed-cell foam application, it's essential to partner with a knowledgeable and experienced closed-cell foam supplier. Our directory of closed-cell foam suppliers features companies with extensive expertise in foam material selection, precision fabrication, and custom conversion services for a variety of industries and use cases.
Each closed-cell foam supplier profile highlights their technical capabilities, equipment, and specialty services, along with a convenient contact form for direct inquiries or quote requests. Use our proprietary website previewer to quickly compare suppliers, review their foam product offerings, and evaluate their suitability for your project.
When evaluating closed-cell foam companies, consider these questions:
- Does the supplier offer the specific foam type, density, and thickness you require?
- Can they provide value-added fabrication (die cutting, CNC routing, laminating, adhesive backing)?
- Do they have experience with your industry or application (medical, automotive, packaging, construction, etc.)?
- Are they able to meet your delivery schedules and volume requirements?
- Can they supply documentation and certifications for compliance or regulatory needs?
Use our easy RFQ (Request for Quote) form to contact multiple closed-cell foam suppliers at once, streamlining your sourcing process. For more information on closed-cell foam materials, manufacturing methods, or application engineering, consult our knowledge base or connect with an expert today.
Looking to get started with your next closed-cell foam project? Start comparing suppliers and request a quote now!



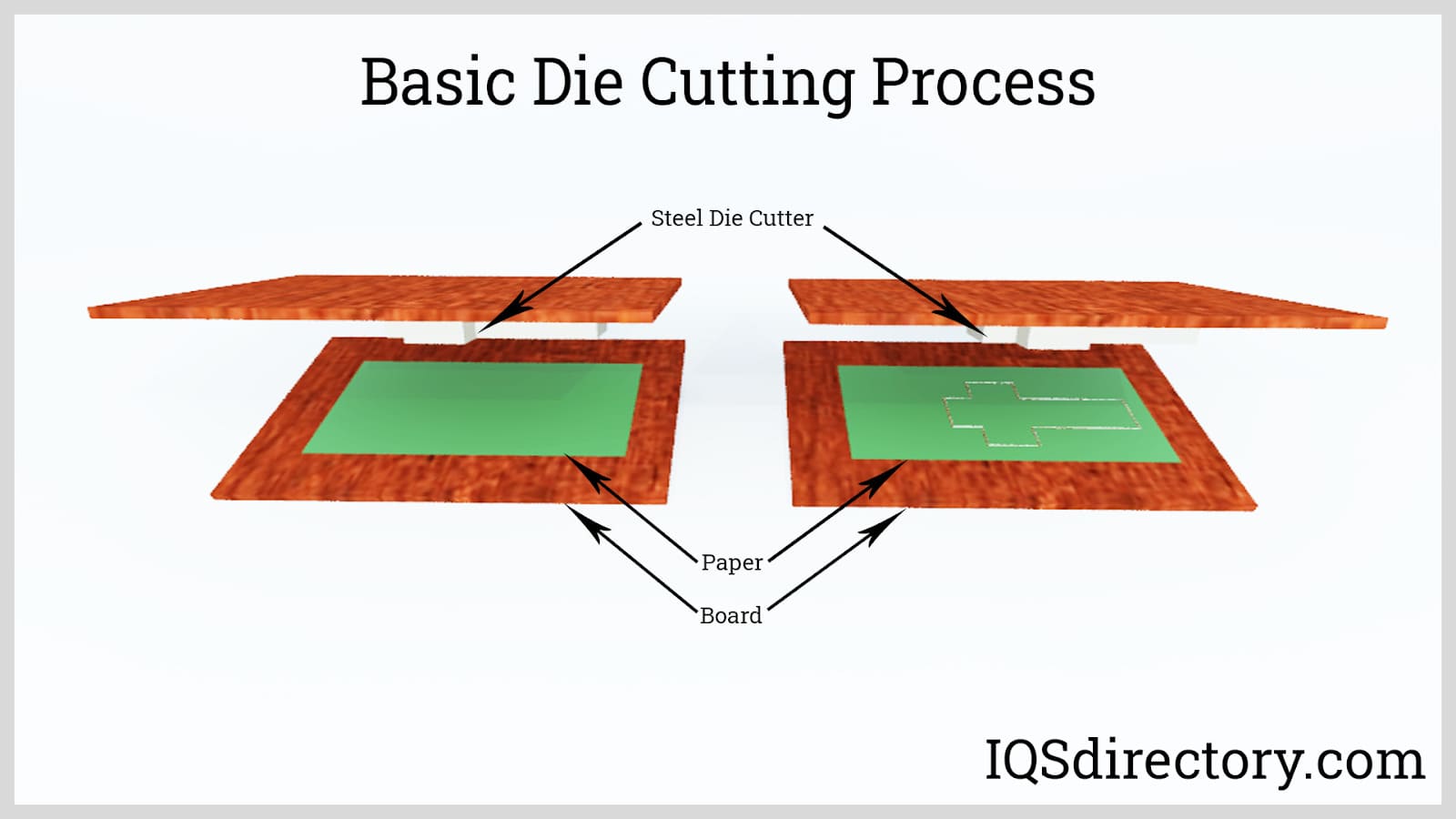

 Die Cutting
Die Cutting Foam Fab
Foam Fab Gaskets
Gaskets O-rings
O-rings Plastic Fabricators
Plastic Fabricators Tape Suppliers
Tape Suppliers Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services